Understanding the Distinctions Between Bees and Wasps
In the buzzing world of insects, two creatures often share the spotlight: bees and wasps. Despite their similarities, these creatures have distinct characteristics that make them unique.
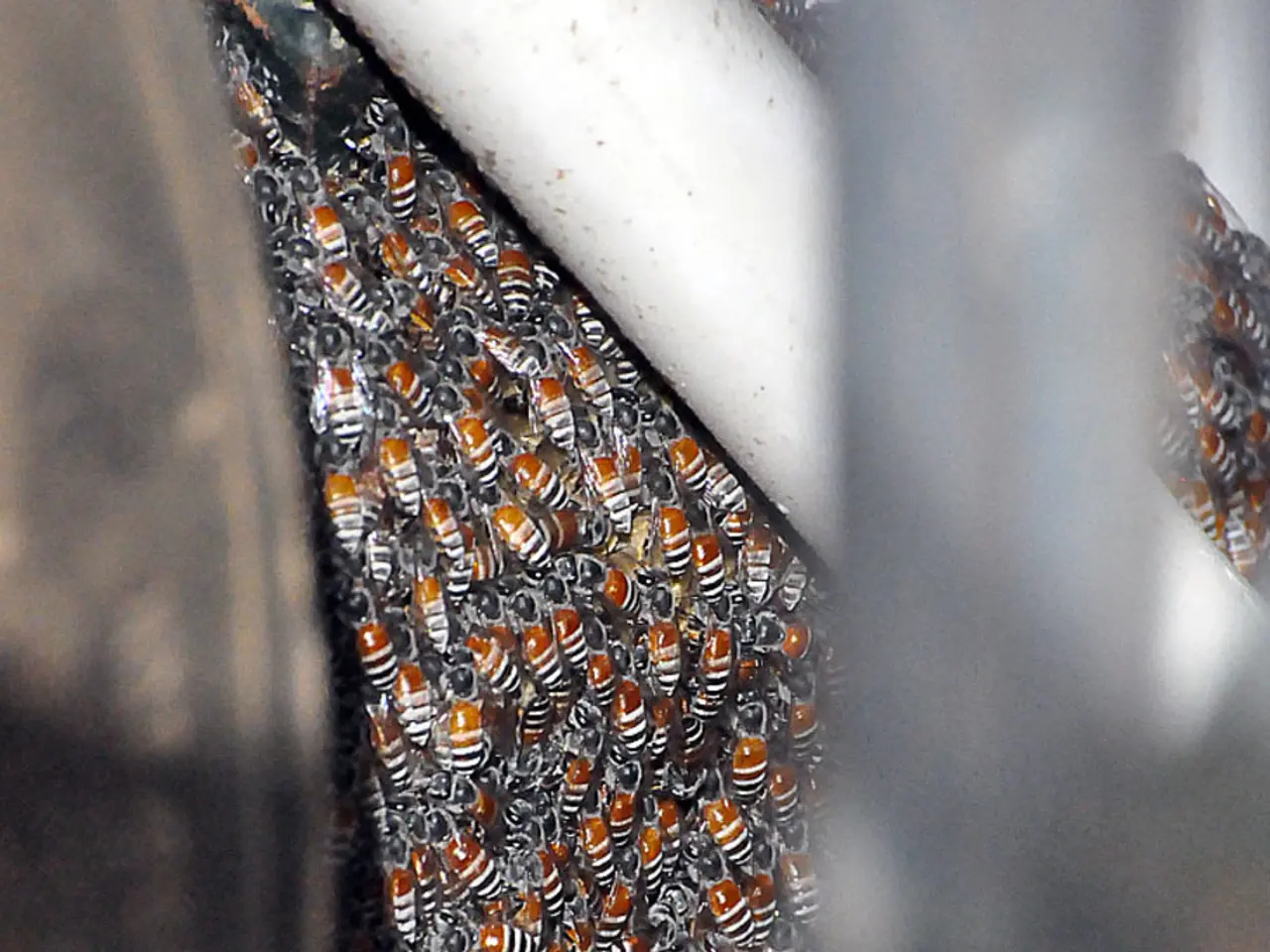
Bees and wasps belong to different families within the order Hymenoptera. Bees, known for their fuzzy bodies and rounded shape, build hives with hexagonal cells made of beeswax. In contrast, wasps construct nests from a paper-like material created by chewing wood fibers mixed with saliva.
The social structure of these insects also varies. Honeybee colonies consist of a queen, workers, and drones, while wasp colonies range from solitary individuals to complex societies with a caste system. Each spring, honeybee queens start new colonies, while bees maintain the same colony and hive throughout the year. Most wasp colonies die off in winter, with only fertilized queens surviving by hibernating until spring.
One of the most significant differences between bees and wasps lies in their defense mechanisms. Honeybees have a barbed stinger that tears away from their body when they sting, making it a one-time defense mechanism. Most other bee species and wasps have smooth stingers that allow them to sting multiple times. Wasp venom is often more potent than bee venom and can cause intense pain and significant systemic reactions. Wasps, particularly species such as yellow jackets and hornets, are known for their more aggressive behavior and are more likely to sting humans unprovoked. Bees, on the other hand, are generally more docile and less aggressive, and they are unlikely to sting unless provoked.
Bees and wasps play different roles in our ecosystems. Bees, as primary pollinators, are incredibly efficient at transferring pollen between flowers, contributing significantly to food production and local economies, especially in agriculture. Wasps, while not as effective at pollination as bees, contribute to pollination in their own way, with certain wasp species, such as fig wasps, being specialized pollinators for specific plants. Wasps also play an essential role in pest control due to their predatory habits, feeding on insects that are harmful to crops and helping regulate pest populations naturally.
Understanding the differences between bees and wasps fosters greater awareness of how to safely interact with them. Respecting their roles and characteristics can lead to a healthier and more harmonious relationship with the natural world. By appreciating the unique qualities of these insects, we can better protect and conserve the diverse ecosystems they inhabit.
Read also:
- Peptide YY (PYY): Exploring its Role in Appetite Suppression, Intestinal Health, and Cognitive Links
- Toddler Health: Rotavirus Signs, Origins, and Potential Complications
- Digestive issues and heart discomfort: Root causes and associated health conditions
- House Infernos: Deadly Hazards Surpassing the Flames