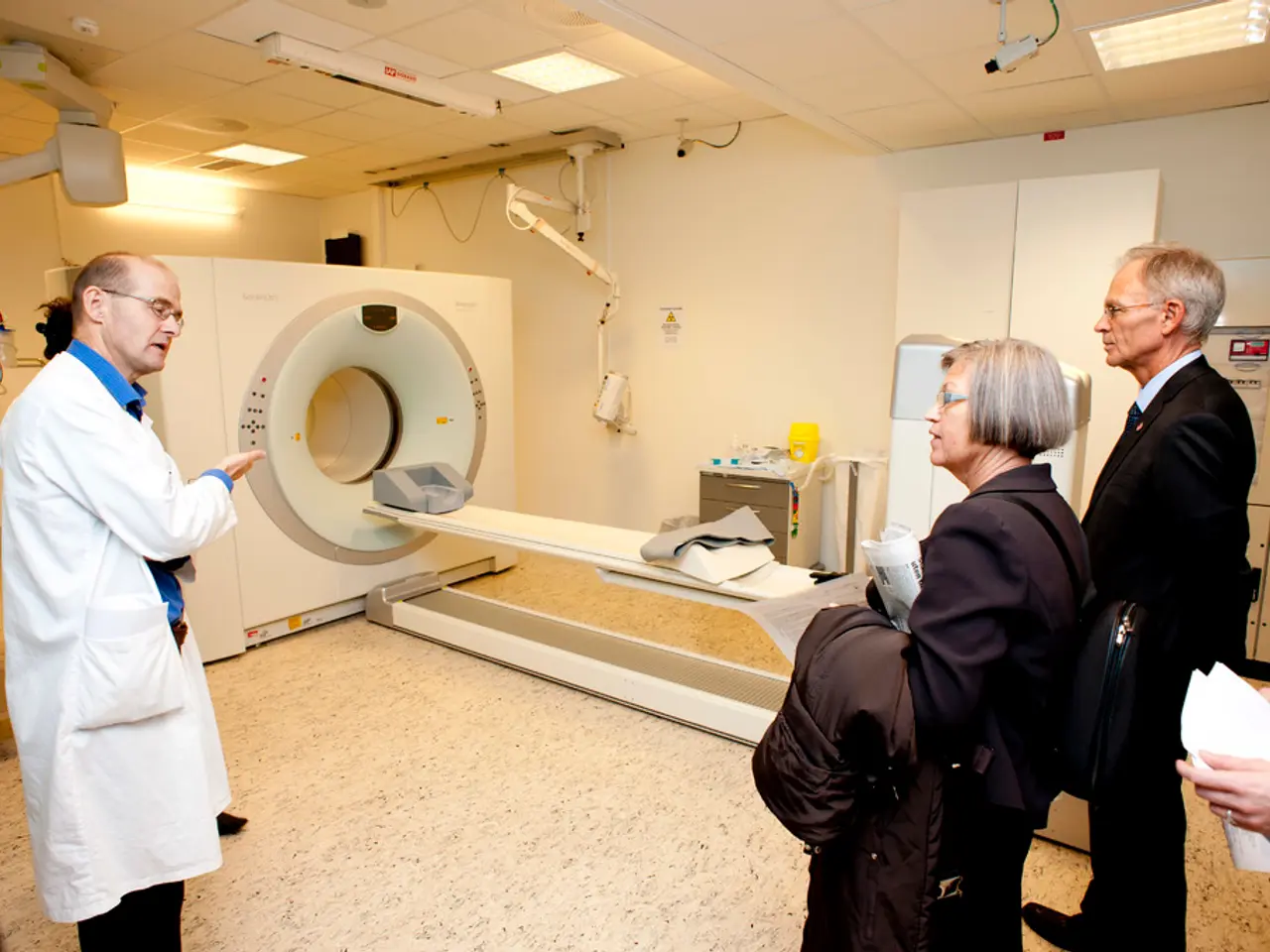
A Pap Test, in simpler terms, is a medical examination used to screen for cervical cancer in women. It involves the collection and microscopic examination of cells from the cervix.
The HPV vaccine, a powerful tool in preventing cervical cancer, is recommended for preteens aged 11 to 12 but can be given up to age 26. Despite this preventative measure, cervical cancer can still occur, and regular screening is essential for its early detection.
The Pap test, a crucial screening procedure, is typically recommended for women starting at the age of 21, regardless of sexual history. During a Pap test, a healthcare provider collects cells from the cervix to check for changes that may indicate the presence of cervical cancer or precancerous conditions.
An abnormal Pap test result indicates that some cells in the cervix appear atypical. This may suggest the presence of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) or other issues that require further investigation. It's essential to remember that not all abnormal results indicate cancer.
If you notice any symptoms after an abnormal Pap test, such as unusual vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, changes in menstrual cycle, pain during intercourse, unusual discharge, symptoms of HPV, or any other unusual symptoms, consult your healthcare provider promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference.
Common questions about abnormal Pap tests include what they mean, the next steps after receiving an abnormal result, and common causes of abnormal results. Support is available through healthcare providers, support groups, and educational websites focused on women's health.
If your initial follow-up tests show the presence of HPV, your doctor may recommend regular monitoring or treatment options, such as LEEP, Cone Biopsy, or Hysterectomy. Understanding the diagnosis process for an abnormal Pap test is crucial for managing your health effectively. This process includes understanding the Pap test, types of abnormal results, initial follow-up steps, and further diagnostic tests such as HPV testing, colposcopy, and biopsy.
Regular screening, including Pap tests, is essential for preventing cervical cancer. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends starting Pap tests at age 21 and having them every three years for women aged 21-29. After treatment, follow-up appointments with regular Pap tests and HPV testing are crucial to ensure the abnormal cells have been effectively removed and to monitor for new abnormalities.
Inflammation or infection, hormonal changes, previous treatments, and smoking can also contribute to an abnormal Pap test result. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly, can play a significant role in reducing the risk of cervical cancer.
The Papanicolaou test (Pap smear) was first used in the United States. During the test, a healthcare provider gently opens the vagina with a speculum and collects cells from the cervix using a small brush or spatula.
Remember, early detection and regular screenings are key to managing cervical health. If you have any concerns or questions about your Pap test results, don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support.
Read also:
- Peptide YY (PYY): Exploring its Role in Appetite Suppression, Intestinal Health, and Cognitive Links
- Toddler Health: Rotavirus Signs, Origins, and Potential Complications
- Digestive issues and heart discomfort: Root causes and associated health conditions
- House Infernos: Deadly Hazards Surpassing the Flames